Introduction
Welcome to the GHOST TestNet 3.1 Launch Guide. In TestNet 2.0 we had 140 Nodes and ability to send $CSPR. With TestNet 3.1 there is a ton of stuff coming including further GHOST Eye updates, staking, slashing, etc. All existing TestNet 2.0 and 3.0 Full Nodes MUST update to TestNet 3.1 to take advantage of new functionality.
1. Prerequisites

Before you can proceed with launching you GHOST Node please make sure to go though the following guide:
- GHOST Chain Startup Guide – create the proper environment and install GHOST Chain.
- Testing Connectivity Guide – test whether or not you node can become a Boot Node and set proper firewall rules.
2. GHOST Chain Key Generation

Start with creating the following directory:
sudo mkdir /etc/ghostGet your username:
whoamiGive the user permission to the directory and substitute {USERNAME} for the one from previous command:
sudo chown {USERNAME} /etc/ghostGenerating Node Keys
To generate the node key use the following command:
~/ghost/ghost-node/target/release/ghost key generate-node-key --bin --file=/etc/ghost/node-key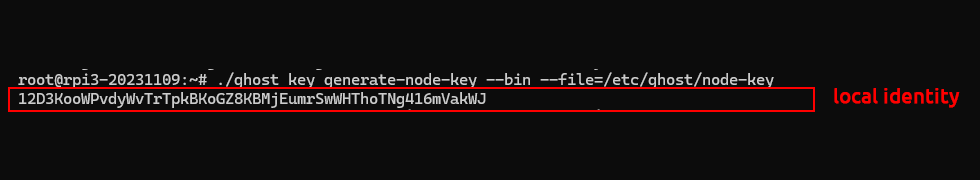
3. Launching GHOST TestNet 3.1

Go to ghost-node directory:
cd ghost/ghost-nodeRemove ghost ledger:
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/ghost/chains/casper_staging_testnetMake sure ghost-node is up to date:
git pull origin mainRecompile ghost-node using starter.sh and --release flag. Make ghost-node service being able to be started by default user using --make-global:
./scripts/starter.sh --release --make-globalThe default option is capitalized which is N, you can also press Enter to choose the default option. In this case we want to recompile so type y and press Enter to proceed:
'cargo build --release ' is what you want? [y/N]:Recompiling will take some time!
Check GHOST Node version, the output should be ghost 0.7.197-8a0cbb94b4d:
ghost --versionCheck checksum the output should be ad653233c978bfd00c5e4525b17628632bc4319c5f5f4b4dcc2f050ef3c3d145:
sha256sum /etc/ghost/casper.jsonCreate running ghost-node service that starts on system boot using --unit-file flag. And we must set up the ghost-node launch command by setting arguments using --set-arguments flag:
./scripts/starter.sh --unit-file --set-argumentsOnly change the defaults if you are advanced otherwise press Enter for the following prompts.
If this is your first node simply press Enter to proceed with the default. If this is your second node you should type a different port here, for example 30334, and then you should open this port on your firewall and create a dedicated port forwarding rule on your router as specified in the Testing Connectivity Guide:
specify p2p protocol TCP port (default: 30333):To choose default options press Enter here:
specify JSON-RPC server TCP port: (default: 9945):
specify the chain specification (default: /etc/ghost/casper.json):
specify node's secret key file for p2p networking (default: /etc/ghost/node-key):It is recommended that you give your node a Name you can recognize:
specify name for the node (default: RANDOM_NAME):Validator Node vs Full Node
GHOST Chain consists of 3 types of nodes:
- Boot Node – a type of node that other nodes can connect to in order to verify their legitimacy
- Validator Node – a type of node that has $GHST Staking Capability
- Archival Node – a type of node that will store the archive of the GHOST Chain ledger
If you want to be a Full Node type y:
disable validator mode? [y/N]: NIf you want to be a Validator Node type N:
disable validator mode? [y/N]: NYou can press Enter here:
enable prometheus? [y/N]:Boot Node
For the following prompt:
list of bootnodes if any:Paste one of the following Boot Node address:
| Boot Node Address | Port Status |
|---|---|
|
Checking port 30334 for https://bootnode69.chain.ghostchain.io...
|
|
Checking port 30333 for https://bootnode70.chain.ghostchain.io...
|
|
Checking port 30333 for https://ghostvision.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30334 for https://ghostvision.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30335 for https://ghostvision.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30333 for http://84.247.181.131...
|
|
Checking port 30333 for http://47.199.13.160...
|
|
Checking port 30334 for http://85.190.242.68...
|
|
Checking port 30334 for http://47.199.13.160...
|
|
Checking port 30335 for http://47.199.13.160...
|
|
Checking port 30336 for http://47.199.13.160...
|
|
Checking port 30337 for http://47.199.13.160...
|
|
Checking port 30333 for http://Fujisan1.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30334 for http://Fujisan2.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30335 for http://Fujisan3.mywire.org...
|
|
Checking port 30336 for http://Fujisan4.mywire.org...
|
Changing unit-file name is optional, otherwise press Enter:
[?] name for the unit file (default: ghost-node.service)IF ERROR and [!] user ghost not found pops up press y:
[!] user ghost not found
[?] do you want to create ghost user? (NOT RECOMMENDED: current root) [y/N]:
[+] make ghost owner of /var/lib/ghost
[+] prepare unit file for the ghost-node.service
[+] reloading systemd because of updated unit fileDO NOT enable ghost-node.service press Enter:
[?] do you want to start the ghost-node.service? [y/N]:DO NOT start ghost-node.service press Enter:
[?] do you want to enable the ghost-node.service? [y/N]:
[+] execution finishedRestart ghost-node:
sudo systemctl restart ghost-nodeEnable ghost-node:
sudo systemctl enable ghost-nodeTo see the logs produced by your ghost-node:
journalctl -f -u ghost-nodeTo exit journalctl -f -u ghost-node Press CTRL + C.
Finally, go to GHOST Telemetry so see your node live on the map.
Congratulations! You have an operational GHOST Node.
Existing Full Nodes Migrating to TestNet 3.1

Only follow this section if you currently have a GHOST TestNet 2.0 or GHOST TestNet 3.0 Full Node.
Stop ghost-node process:
sudo systemctl stop ghost-nodeRemove old GHOST TestNet Ledger:
sudo rm -r /var/lib/ghost/chains/casper_staging_testnetGo to ghost-node directory:
cd /home/ghost/ghost-nodePull the most recent GHOST Chain PR from GHOST GIT:
git pull origin mainRecompile your GHOST Node:
./scripts/starter.sh --release --make-globalCheck GHOST Node version, the output should be ghost 0.7.197-8a0cbb94b4d:
ghost --versionCheck checksum the output should be ad653233c978bfd00c5e4525b17628632bc4319c5f5f4b4dcc2f050ef3c3d145:
sha256sum /etc/ghost/casper.jsonRestart GHOST Node:
sudo systemctl restart ghost-nodeCheck GHOST Node log:
journalctl -f -u ghost-nodeTroubleshooting

For future troubleshooting be aware of the following commands:
Update GHOST Node
Go to GHOST directory:
cd ghost/ghost-nodePull the most recent GHOST Node Repo:
git pull origin mainSet arguments. In one of the prompts it is recommended that you give your node a Name you can recognize:
./scripts/starter.sh --set-arguments
## do all stepsCheck GHOST Node log:
journalctl -f -u ghost-nodeTo exit journalctl -f -u ghost-node Press CTRL + C.
Delete GHOST Chain ledger
sudo systemctl stop ghost-nodesudo rm -rf /var/lib/ghost./scripts/starter.sh --unit-filesudo systemctl start ghost-nodeCheck session keys
./scripts/starter.sh --check-keys --insert-keyssudo ls -l /var/lib/ghost/chains/casper_staging_testnet/keystore/sudo systemctl restart ghost-node.serviceSystemd-journal Permission
Find your user:
whoamiReplace $USER with your user:
sudo usermod -aG systemd-journal $USERReplace $USER with your user:
sudo usermod -aG adm $USERCreate new group:
newgrp systemd-journalTo see the logs produced by your ghost-node:
journalctl -f -u ghost-nodeMiscellaneous
To soft reload the entire system:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadTo stop ghost-node:
sudo systemctl stop ghost-nodeTo restart ghost-node:
sudo systemctl restart ghost-nodeTo see the logs produced by your ghost-node:
journalctl -f -u ghost-node![You are currently viewing Launching GHOST TestNet 3.1 [~1 HR]](https://blog.ghostchain.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Launching-GHOST-TestNet-3.1-Featured-Image.png)

![Read more about the article GHOST Chain Testing Connectivity [~1 HR]](https://blog.ghostchain.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/GHOST-Chain-Testing-Connectivity-300x157.png)
