Introduction
GHOST Chain consists of 3 types of nodes:
- Boot Node – a type of node that other nodes can connect to in order to verify their legitimacy
- Validator Node – a type of node that has $GHST Staking Capability
- Archival Node – a type of node that will store the archive of the GHOST Chain ledger
Boot Nodes act as a form of security layer for the network. If a Validator Node wants to join the GHOST Chain network it can only do so if the Node Operator is given the needed key to be verified by a Boot Node. After the verification is complete, the Validator Node can begin validating transactions along other Validator Nodes. The network can have multiple Boot Nodes therefore multiple points of entry.
In this guide we will be testing connectivity between your node and the GHOST Chain Boot Node. The idea is for the GHOST team to make sure that existing Boot Nodes can be connected from any part of the world. We will also test the ability for your node to be a Boot Node for other Validator Nodes.
By now you should have followed the instructions outlined in the GHOST Chain Startup Guide.
1. Validator Node Qualification Test [OPTIONAL]

Becoming a Validator Node on GHOST Chain is an absolute MUST if we want the network to be sufficiently decentralized. However, due to certain ISP limitations some countries make it being a Validator Node easier than others. Hence, the GHOST Dev team came up with a Validator Node Qualification Test.
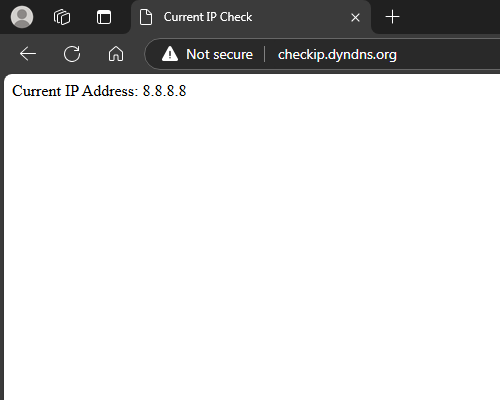
First we must determine the public IP for your GHOST Node Machine. You can open the FireFox browser on your GHOST Node and go to CHECK IP.
You should see something like this:
Then open terminal on your GHOST Node machine and install TRACEROUTE:
sudo apt install tracerouteThen type the following command replacing YOUR_IP_FROM_PREVIOUS_STEP with an actual IP address from previous step:
traceroute YOUR_IP_FROM_PREVIOUS_STEPPress Enter and let the command run for a while.
If your GHOST Node is not behind a NAT your terminal window should look something like this:
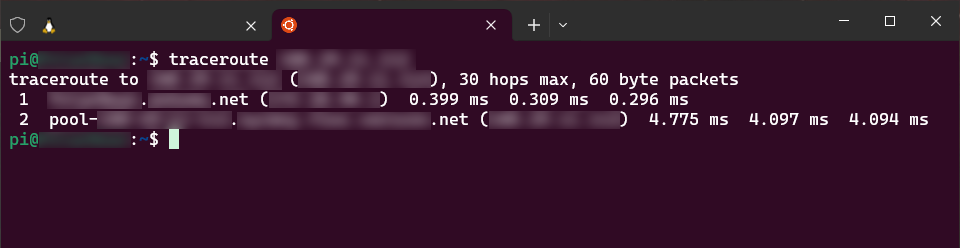
If your GHOST Node is behind NAT your terminal window should look something like this:
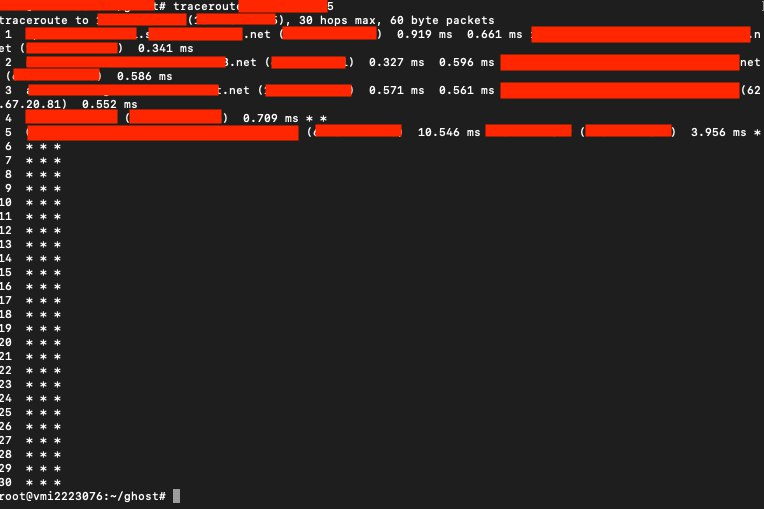
If your GHOST Node is NOT behind the NAT then your node can be a Boot Node. If your GHOST Node is behind the NAT then your node CANNOT be a Boot Node and you will have to use some kind of a proxy to rectify the situation.
Afterwards, post the screenshot of your terminal window in the Whales group. Feel free to blur out your IP.
2. Setting Proper Firewall Rules

You must enable port 30333 on your router
Based on prior instructions you may have configured your firewall in way that is no longer needed. For the purpose of GHOST Chain you should only open port 30333 port and close other ports.
Checking Firewall
Check the ports that are opened on your firewall:
sudo ufw numberedIf port 9945 is opened then close it:
sudo ufw deny 9945Configuring Router
Enable port forwarding for port 30333 on your router. Be mindful that different networks and routers have different ways of setting this up. It is best to search for portforwarding instruction for hte specific router model. For example, here is a video describing how to set up a port forwarding rule for port 8000 on Huawei Routers:
![You are currently viewing GHOST Chain Testing Connectivity [~1 HR]](https://blog.ghostchain.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/GHOST-Chain-Testing-Connectivity.png)
![Read more about the article GHOST Chain Startup Guide [~ 4HRS]](https://blog.ghostchain.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/GHOST-Chain-Startup-Featured-Image-300x157.png)

